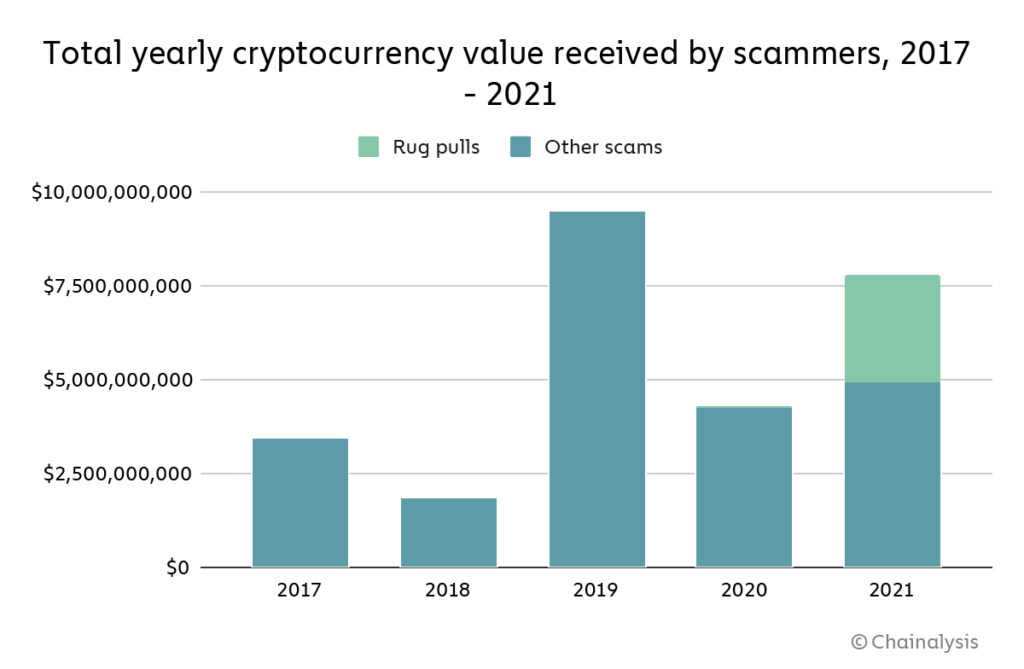
cryptocurrency Scam
Cryptocurrency fraud is a type of financial crime involving the use of digital currencies, such as
Bitcoin. It can involve the theft of digital currency, the sale of fake digital currency, or the use of
digital currency to facilitate illegal activities. It often occurs through online platforms and
exchanges, but it can also occur through other methods such as phishing, malware, and ransomware.
Cryptocurrency scams are very common in the digital currency market. These scams involve a variety of
methods, including phishing scams, fake ICOs, Ponzi schemes, and pump-and-dump schemes.
How do cryptocurrency scams work?
Cryptocurrency scams typically involve a scammer convincing victims to send money or cryptocurrency in exchange for something of greater value, such as investments, rewards, or services. The scammer then disappears with the funds. They may also use phishing scams to gain access to victims' wallets and steal their funds. Additionally, some scammers create fake cryptocurrency exchanges or wallets, promising low fees or high returns, and then disappear with victims' funds.

some exchanges may be fraudulent and used to steal money from unsuspecting users. It is important to be aware of these scams and take steps to protect yourself from them. Be sure to do your research before investing in any digital currency and only purchase from trusted sources. Additionally, always be sure to keep your personal information safe and secure.
How to protect from Cryptocurrency Scams
- Use cold storage: Cold storage refers to storing your cryptocurrency offline in a secure environment. This is typically done through a hardware wallet or paper wallet, which can be stored in a safe or safe deposit box.
- Use two-factor authentication (2FA): Two-factor authentication is a security measure that requires two different methods of authentication to access your account. This could be something like a password and a one-time code sent to your mobile phone.
- Use a strong password: Create a strong and unique password for any cryptocurrency accounts. Avoid using words that can be found in a dictionary, and try to use a mixture of numbers, letters, and symbols.
- Use an encrypted messaging system: Encrypted messaging systems allow you to communicate with other users securely. This can help prevent your messages from being intercepted by hackers.
- Keep your software up to date: Ensure that you have the latest version of your wallet software and any other cryptocurrency applications you use. This will help protect you from any known security vulnerabilities.
- Only use trusted exchanges: Stick to trusted exchanges when trading cryptocurrencies to ensure that your funds are safe and secure.
- Be aware of scams: Be aware of
People use cryptocurrency to make purchases, transfer funds, store value, and speculate on price
movements in the market. Cryptocurrency can be used to pay for goods and services, or it can be traded
on exchanges.
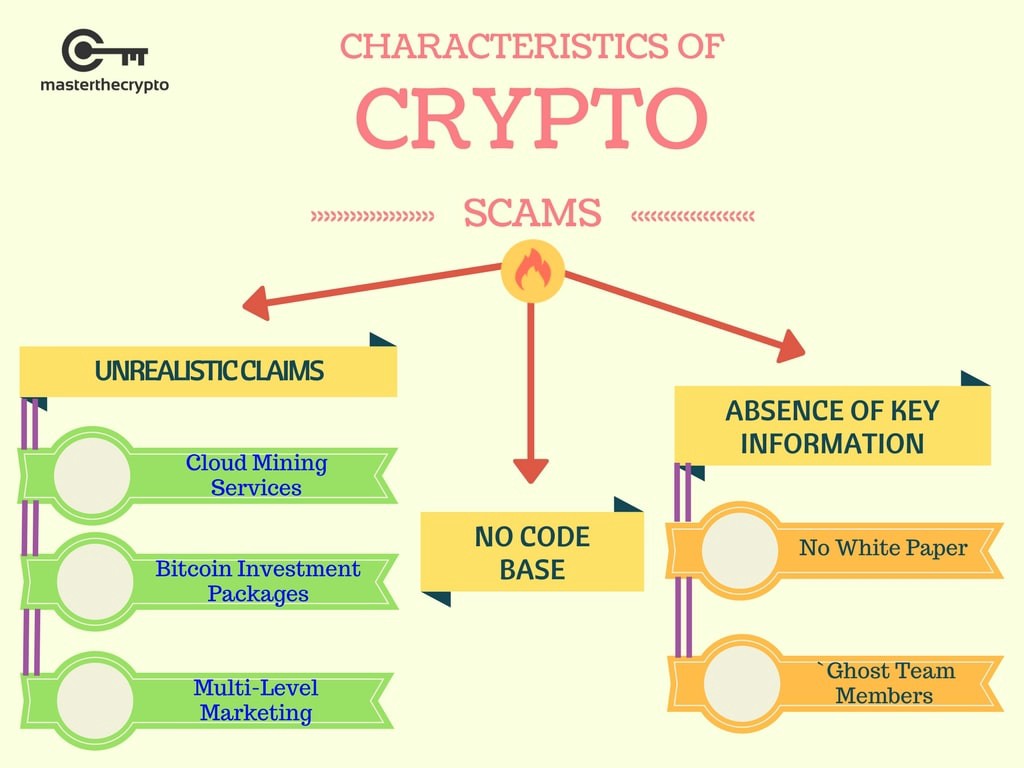
Many people use cryptocurrency as an alternative to fiat money, as it can provide more privacy and security than traditional banking systems. There are also many people who use cryptocurrency as a form of investment, as the value of some digital currencies has grown significantly over the last few years.
Paying With Cryptocurrency ?
- Reduced Transaction Costs: One of the biggest advantages of using cryptocurrency is that transactions are typically low cost and fast. This is because there are no third-party intermediaries involved in the transaction process and it's just the two parties involved in the transaction.
- Increased Security: Cryptocurrency transactions are also more secure than traditional payments. This is because the transactions are encrypted and stored on a distributed ledger, which makes it difficult for hackers to access the data and steal funds.
- Greater Anonymity: Unlike traditional payments, cryptocurrency transactions offer greater levels of privacy and anonymity. This is because the transactions are pseudonymous and don't require users to reveal their identity.
- Increased Accessibility: One of the best advantages of cryptocurrencies is that they are accessible to anyone with an internet connection. This makes it easier for people in developing countries, who may not have access to traditional banking services, to access financial services.
How To Avoid Cryptocurrency Scams?
- Do your research: Before investing in any cryptocurrency, it's always a good idea to do your research and make sure that the project is legitimate. Check out reviews from other investors, read the project's white paper, and visit their website to get a good understanding of how the project works.
- Don't trust too easily: Be sure to double-check any requests for funds or investments or promises of guaranteed returns. It's also important to be aware of any red flags such as overly-aggressive marketing tactics, anonymous team members, and unrealistic claims.
- Be wary of free offers: If a free coin or token is being offered, it's almost certainly a scam.
- Don't invest more than you can afford: Cryptocurrency investments can be volatile and risky, so it's important to only invest what you can afford to lose.
- Use secure wallets: Make sure to use a secure wallet to store your cryptocurrencies, and be sure to back up your wallet in case of loss or theft.
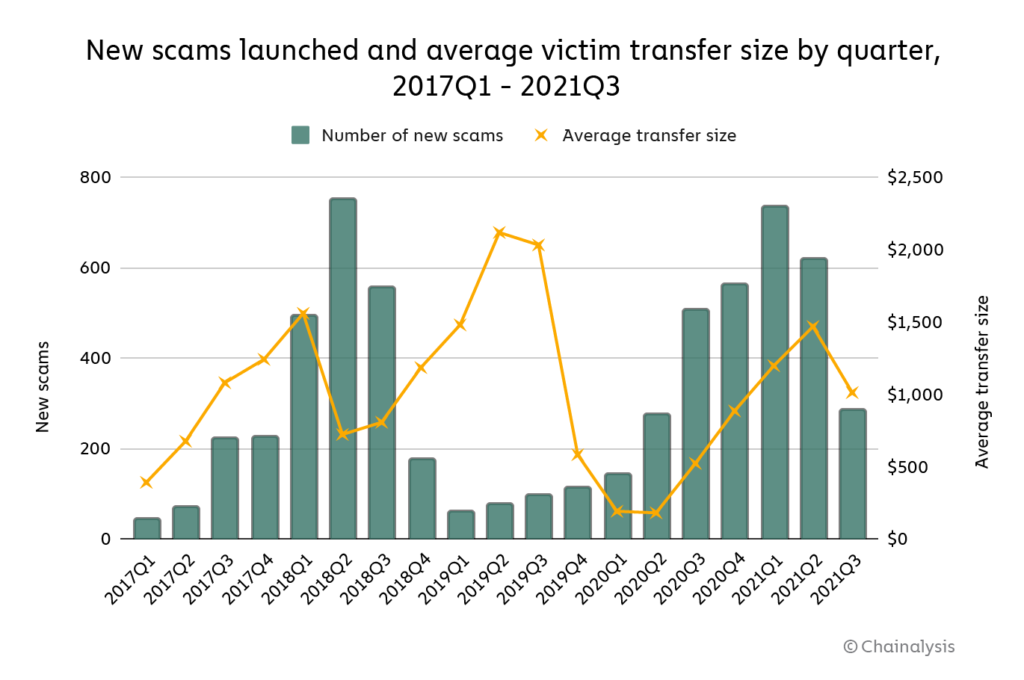
Fake cryptocurrency exchanges are websites or exchanges that pretend to offer legitimate cryptocurrency services, such as trading and exchanging digital currencies, when in fact they are fraudulent and designed to scam users.
Fake cryptocurrency Exchanges :
Fake exchanges often make promises of high returns and low fees, but they are not able to deliver. They also often require users to provide personal information, such as their email address, phone number, and bank account details.
- CryptoNet
- CryptoBarter
- BitTradeX
- CryptoXchange
- CryptoCoinage
- CryptoCoinCentral
- Crypto Spot Exchange
- Crypto Trade Exchange
- CryptoXplore
- CryptoCurrency Exchange
Cryptocurrency uses blockchain for verification and does not run through financial institutions, so it is harder to recover from theft
How to spot cryptocurrency scams ?
Unsolicited emails: If you receive an unsolicited email, text, or social media message from someone claiming to be a cryptocurrency expert, it is likely a scam.
Fake websites: Be wary of any websites or online services offering "amazing" returns on cryptocurrency investments.
Unregulated exchanges: Cryptocurrency exchanges that are not regulated by any government or banking institution are often used by scammers to hide their activities.

Unsolicited offers: If someone is offering a "once-in-a-lifetime" opportunity to get involved in cryptocurrency trading, it is likely a scam.
Pressure to invest quickly: If someone is pressuring you to invest quickly in cryptocurrency, it is likely a scam.